A green solution for municipal solid waste

In its endeavor to explore and progress technologies for sustainable urbanism, the 3RINCs conference convenes each spring, bringing together Asian experts working at the forefront of 3R technologies and systems today.
An annual event since 2014, the 3RINCs conference promotes proper waste management across the globe by focusing on the three 'Rs': reduce, reuse and recycle. The conference is held up as a platform for key stakeholders to engage and push the envelope forward on advancing sustainable solutions for our rapidly urbanizing world.
A proud sponsor since the beginning, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Environmental & Chemical Engineering Co. (MHIEC) is a key stakeholder, promoting sustainability principles not only as a sponsor but also through its unique and cutting-edge research and development into new technology in the sector.
Dealing with municipal solid waste
Innovative waste-to-energy technology is heralded as a sustainable and necessary solution to the increase in waste due to rapid urbanization; adequate waste disposal facilities are crucial not only for public health but also preserving the natural environment.
Take Japan as an example, which accumulates some 43 million tons of waste each year. Much of it is processed by more than 1,100 waste incineration facilities throughout the country, which have become indispensable for their role in seamlessly handling all the garbage. The waste is incinerated, harmful substances are detoxified and the collective output is then effectively harnessed into thermal energy, thereby becoming an important source of power. As a result, only around 10% of municipal solid waste needs to go to landfills.
Many of these waste-to-energy facilities are designed and built by MHIEC and are superior in that they are highly adaptable and able to handle various types of waste, including plastics. They are also an efficient source of alternative energy, using for fuel what would otherwise had been an environmental problem.
The country is known for being clean, but while the locals’ good manners are often in the spotlight, waste treatment technologies can take part of the credit.
One man's trash
MHIEC's waste-to-energy facilities are notably efficient for power generation. According to MHIEC's team of engineers in Japan, the company has commercialized high-temperature, high-pressure boilers that convert waste to energy both quickly and efficiently.
This particular technology generates diverse outputs. The energy that is produced is sold to public electricity grids, with the exception of energy consumption on-site. The incinerated ash also yields raw material that can be used for cement, by using proprietary technology. What's more, MHIEC's waste-to-energy facilities can successfully treat solid waste, sewage sludge, industrial waste and biomass.
Misconceptions over waste-to-energy facilities in the past were common and widespread. The white smoke exiting the facilities, for example, was often mistaken the for toxic emissions, but in reality it is a clean and non-harmful phenomenon created when water vapor comes into contact with the lower temperature of the atmosphere.
The combustion at MHIEC's plants is also managed to prevent air pollution through advanced flue gas treatment, a process specifically designed to reduce the amount of pollutants emitted by waste-to-energy facilities. MHIEC's plants have a record of high performance for the removal of chemicals like hydrochloride, sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxide and dust in the flue gas. Emissions at the waste-to-energy facilities are significantly below the regulations set by European emissions standards.
Global success
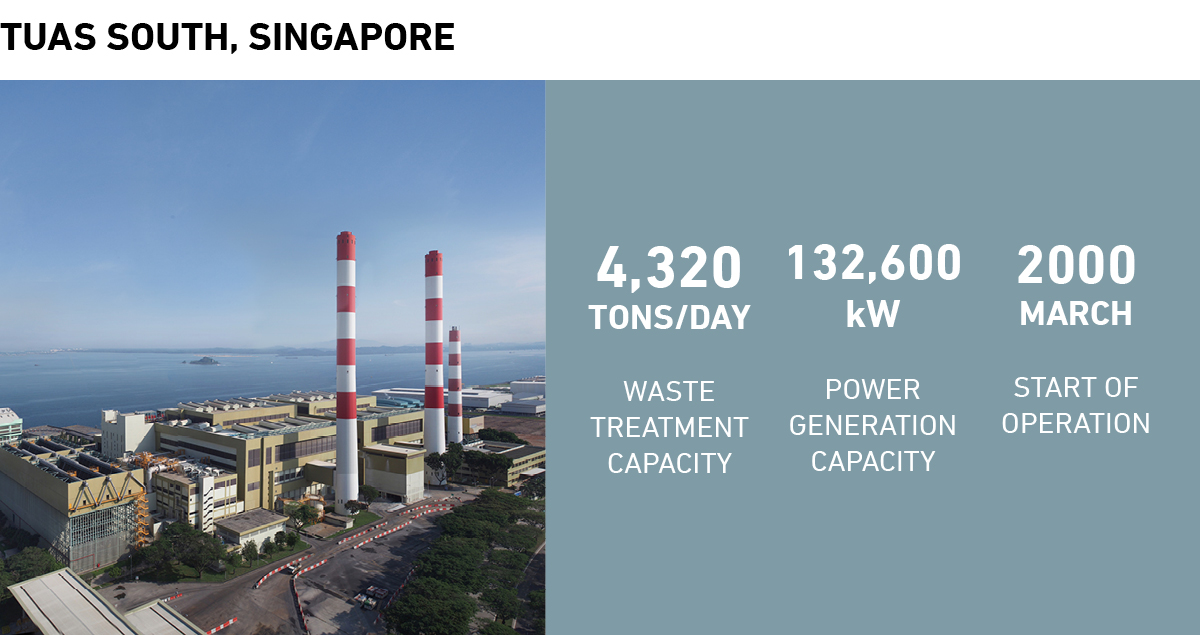
Since 1964, MHIEC has delivered more than 300 advanced, reliable waste treatment plants around the world, extending its successful track record globally. Of MHIEC's approximately 320 total waste treatment facilities, 280 are in Japan. The country is known for being clean, but while the locals' good manners are often in the spotlight, waste treatment technologies can take part of the credit. And MHIEC's technologies are making considerable contributions in other countries as well.


Always looking to improve the technology, the company is currently developing AI and IoT technology, which will allow for greater remote support so that the facilities can be managed by a smaller number of people. A project with the city of Yokohama has already seen the effort to be promising. At the same time, the company is also developing "InteRSePT", a cyber security technology to ensure the safekeeping of control systems.
Already established as a leader in waste-to-energy technology with facilities throughout Asia, MHIEC is now building the world's largest plant of its kind in Shanghai, China, due for completion in 2019.
More on technologies to solve urbanization issues MHI Environmental & Chemical Engineering





